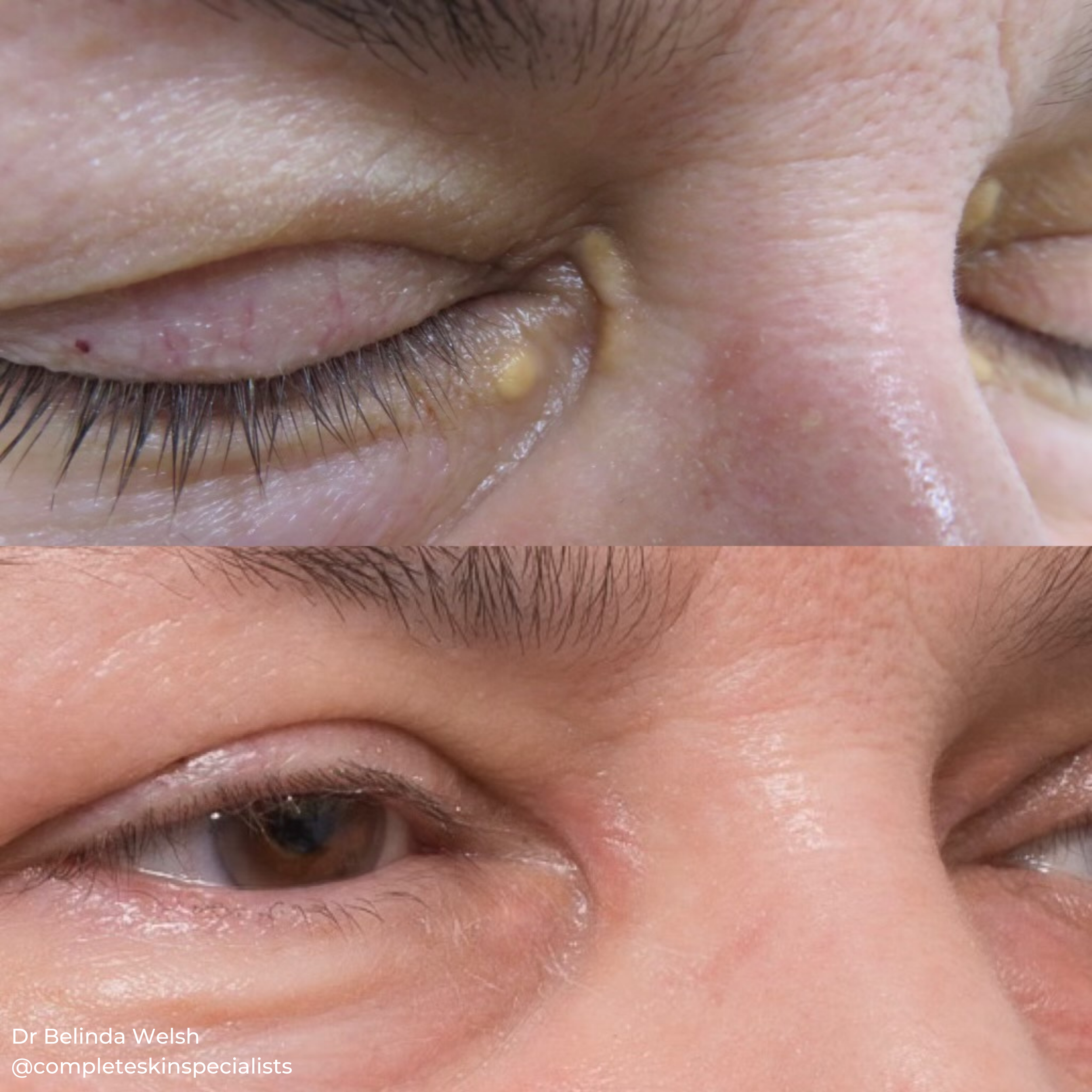
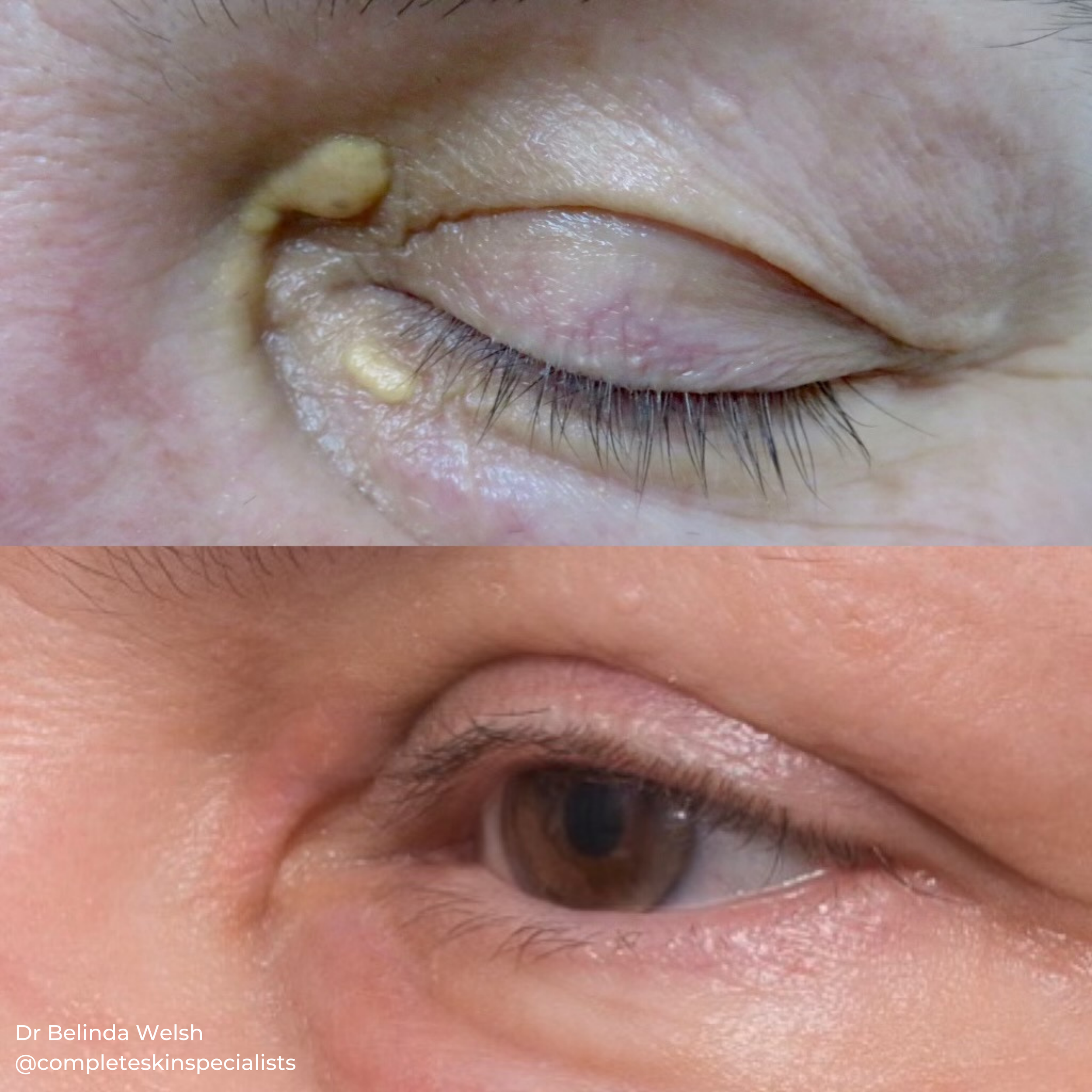
Xanthelasma
-
Xanthelasma are yellowish, cholesterol-rich deposits that appear on the eyelids and around the eyes. While they are generally harmless, they can be a cosmetic concern for many individuals.
There are a number of genetic and lifestyle factors which contribute to the development of Xanthelasma. High levels of cholesterol and other fats in the blood can contribute to the development of xanthelasma in some but not all people. A family history of xanthelasma can also increase the likelihood of developing these deposits. Underlying medical conditions such as diabetes, liver disease, and certain lipid disorders are associated with xanthelasma. The condition is also more common in middle-aged and older adults and tends to occur more frequently in women.
-
A thorough evaluation by Dr Welsh is necessary to determine the most appropriate treatment option based on the size, number, and location of the xanthelasma, as well as your overall health.
TCA (Trichloroacetic acid) peels are a common treatment option. TCA is a chemical peel that works by exfoliating the outer layers of the skin, including the xanthelasma deposits. The TCA liquid is carefully applied to the affected area, causing the top layer of skin to peel off over time. This is an ideal non-invasive option with minimal downtime (roughly 1-2 weeks) and effective for small thin lesions.
In many cases, ablative lasers, such as CO2 laser, is used to remove the xanthelasma by vaporizing the top layers of the skin. Dr Welsh has significant experience with CO2 laser in this condition The laser targets the affected area with precision, reducing the risk of damage to surrounding tissues. CO2 laser is effective for larger or multiple lesions. CO2 laser can also be used to treat the skin surrounding the eyes for a broader rejuvenation if needed. Healing can take up to 3 weeks depending on the size of the lesions.
Managing underlying conditions such as high cholesterol or diabetes can help prevent the recurrence of xanthelasma. This may involve dietary changes, medication, and regular monitoring of lipid levels. Each treatment option has its own benefits and risks, and the choice of treatment will depend on individual patient factors. Dr Welsh will discuss all these options with you to determine the best approach for your specific case.